Organizing metadata
This page will cover how the metadata off-chain can be linked to on-chain data and what options you have to better organize your metadata URIs
Dynamic and static metadata URI
The distinction between static and dynamic metadata URI applies only for default_token_uri field inside the token factory. By specifying one of the possible dynamic values inside the default_token_uri the URI will automatically be considered as dynamic for the purposes of searching the token metadata as described in the section below.
If no dynamic value is used inside default_token_uri then this URI will be considered static.
Acceptable dynamic URI values:
factory_id- Factory ID based on the on-chain dataserial_number- Serial number of a specific token. Incremental value starting from 1id- ID of the token. Pool of possible IDs is shared between all Uniqs and in general you won't know it until the token is mintedhash- Hash of the token metadata stored per token
Example of static default token URI: http://myfactory.io/deafult_token.json
Example of dynamic default token URI: http://myfactory.io/{serial_number}.json
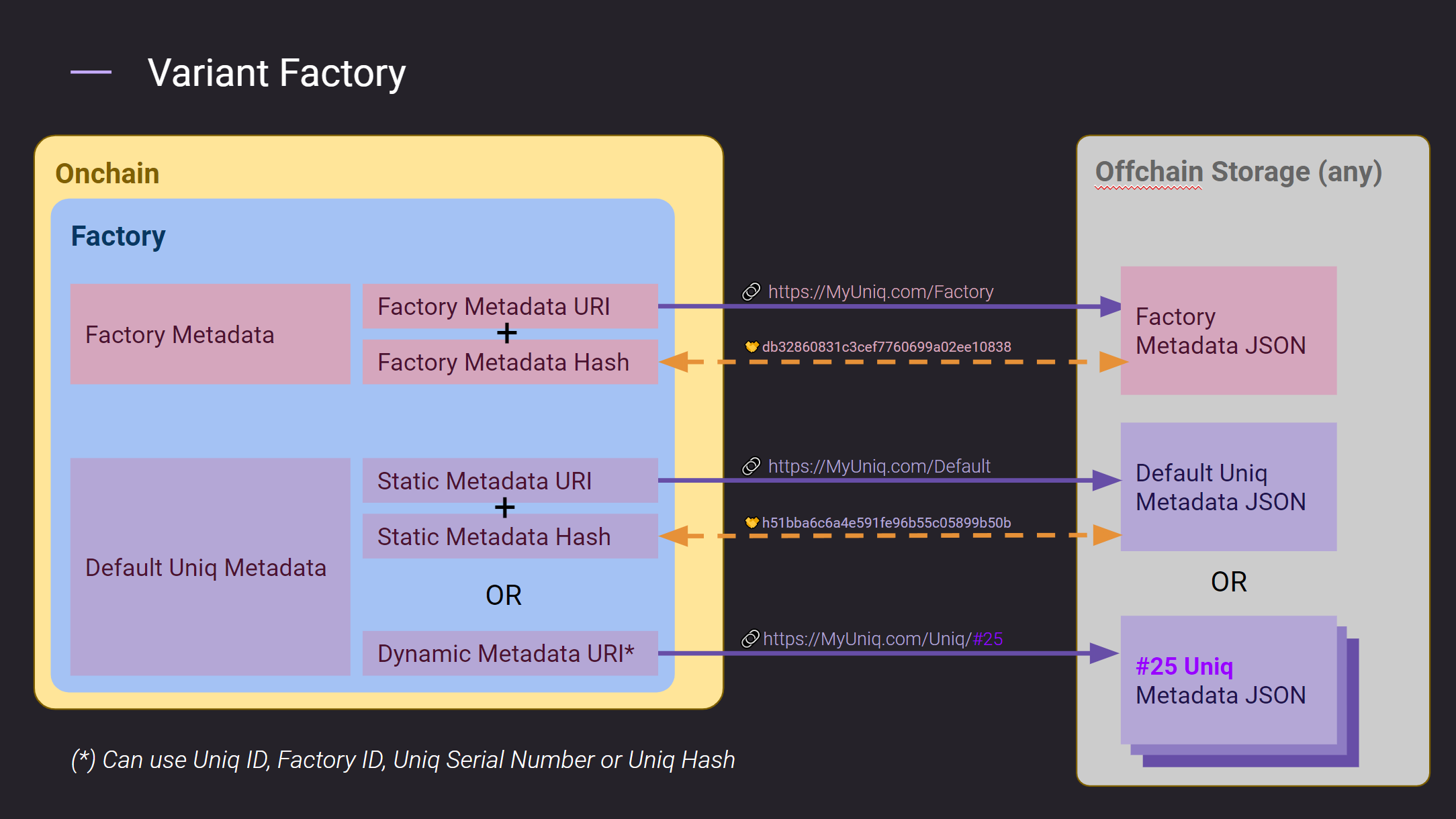
How to set factory metadata
Factory can contain two different types of metadata URI: factory metadata URI and default uniq metadata. Factory metadata URI must always be provided and point to a single JSON metadata file. Factory metadata hash must also be provided and be a hash of the metadata file pointed by factory metadata URI.
For default token URI there is a flexibility in choosing between static and dynamic default token URI (the difference is explained above) but you must always specify some default token URI. For static default token URI you have a possibility to also specify a hash, but for dynamic default token URI you should not be providing hash since dynamic URI implies the possibility that it points to multiple different metadata files depending on the context and thus a single hash cannot fully describe the provenance of metadata files.
The following diagram displays potential use cases when setting factory URIs:
Token factory metadata can be specified during creation - create.b
Following actions are used to change factory metadata URIs and hashes after creation: setmeta.bsetdflttkn
How to set token metadata
You have an option to provide a metadata URI and hash for each token individually. In this case there will be no need to fallback to default token URI inside the token factory.
Both the URI and hash are optional. You may want to provide either of them or both of them at the same time depending on your use case. Refer to this page for details: use cases
Token metadata can be specified when minting a token - issue.b
Alternatively URI and hash can be changed after the token is minted using the following action - settknmeta
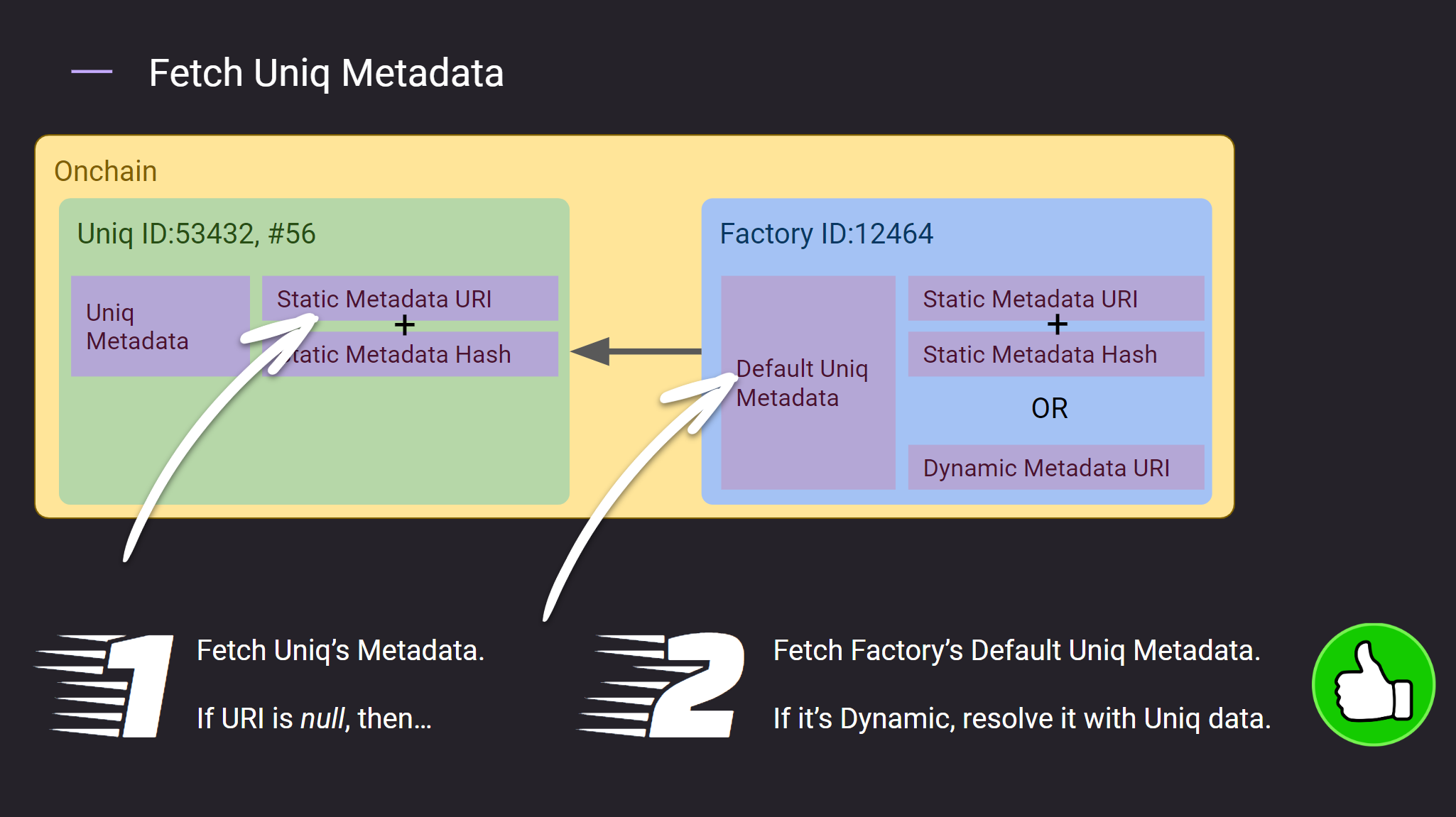
How to find metadata for a given Uniq
For the integrators it may be important to know how to fetch the token metadata if you already know the on-chain token data.
The first step is to check if there is a URI specified on the token itself by checking the uri field of the token. If it is specified then you are done - go to uri and fetch the metadata.
In case the uri is empty or points to an invalid file you need to fallback to default token URI stored inside the token factory. Token factory ID is available in the token data and by querying the factory.b table you will be able to access it's default_token_uri field.
Then depending on if default_token_uri is dynamic or not one of two following paths should be used:
default_token_uriisstatic- go to the URI pointed bydefault_token_uriand fetch the metadatadefault_token_uriisdynamic- substitute all dynamic values inside the URI with information available in the token data (e.g. serial number) and then fetch the metadata using the generated URI.
Refer to the following diagram for details: