How to read the Block Explorer
A block explorer is a web tool that allows users to view information about cryptocurrency transactions and blockchain data. It provides details such as transaction history, wallet balances, and block information, enhancing transparency and accountability.
Our Explorers
Usage
In most cases the search bar at the top takes any of the following:
- Account Name
- Transaction ID
- Block Number
Example Queries
Examples
account:eosio.token
receiver:eosio.token (data.from:eoscanadacom OR data.to:eoscanadacom)
(auth:eoscanadacom OR receiver:eoscanadacom)
account:eosio.token action:transfer
(ram.consumed:eoscanadacom OR ram.released:eoscanadacom)
receiver:eosio.token
db.table:globalExamples pulled from dFuse Docs
Account Page
Account Balance
Account balance is available at the top.
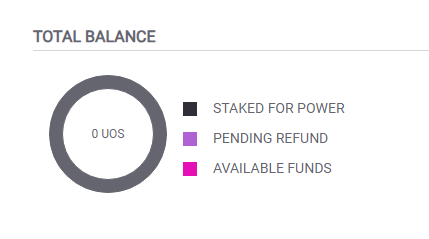
RAM & Power
Both of these are available on the account page as well.
∞ means the account has no limitations. Otherwise, most accounts have a limitation.
Storing data on-chain costs RAM.
Executing transactions utilizes POWER.
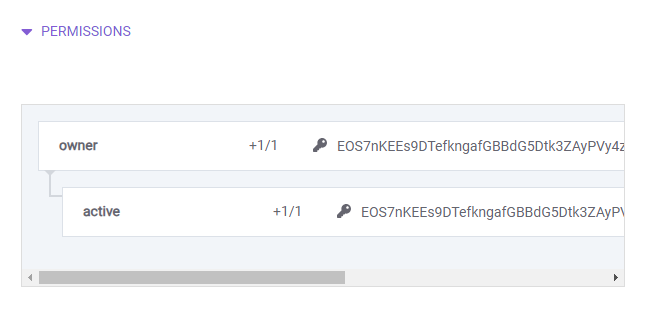
Permissions
You can see who owns an account, or what key has control over an account under the permissions section.
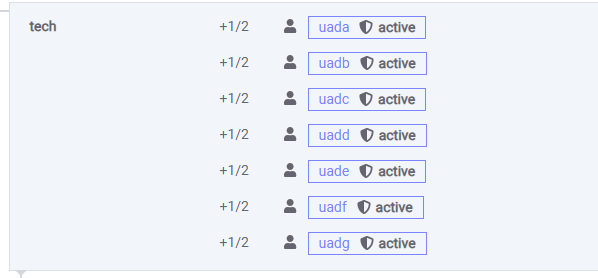
The +1/1 shows how many signatures are necessary to act on behalf of a permission. Permission being active or owner in the example below.
In the example below the tech permission requires two users to a transaction to act on behalf of the ultra@tech account.
Contracts
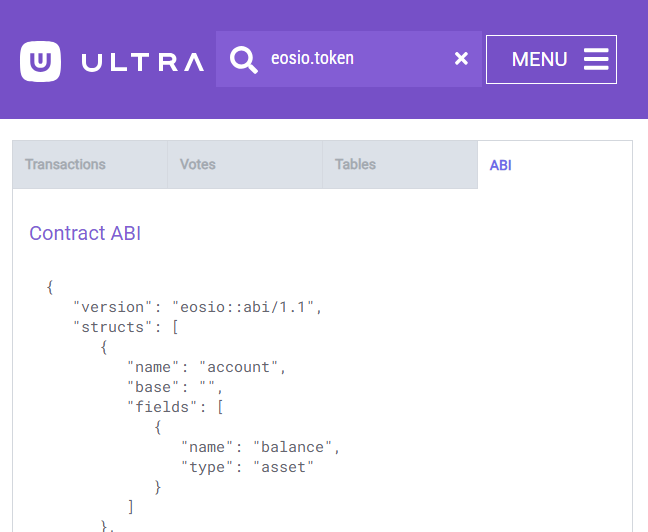
When you are on an account page such as eosio.token you can see that it has a contract deployed because it has the tables and ABI tabs.
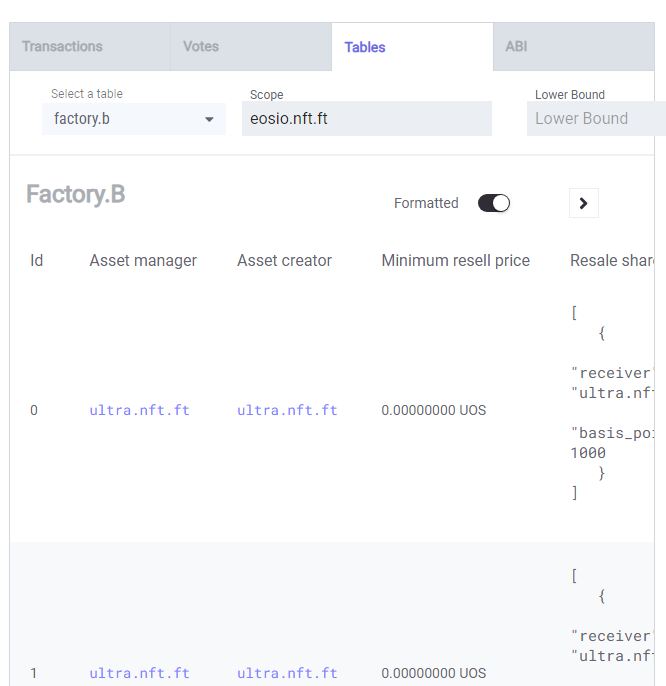
Tables
Tables can be browsed for additional information if you're aware of how the table is structured. In the case of eosio.nft.ft I can view the factory.b table to see available Uniqs. Tables available can be gathered from the abi tab.
It's highly recommended to use curl requests against REST API Endpoints when reading data, or write a small script in one of your favorite programming languages.